Preauricular fistula
OVERVIEW
What is preauricular fistula?
Preauricular fistula is mostly a congenital disease caused by maldevelopment of ear structures during the embryonic stage and is a type of congenital genetic disorder[1].
Main manifestations include: the fistula opening is usually located in front of the crus of the helix (the helix is the outermost curled part of the auricle), often without obvious clinical symptoms, with only localized itching and white discharge[2]. In cases of infection, symptoms may include localized redness, swelling, pain, and pus discharge.
No treatment is required when there are no obvious clinical symptoms. If infection occurs, antibiotics can be used to control it, followed by surgical excision, which is often curative with a good prognosis[3].
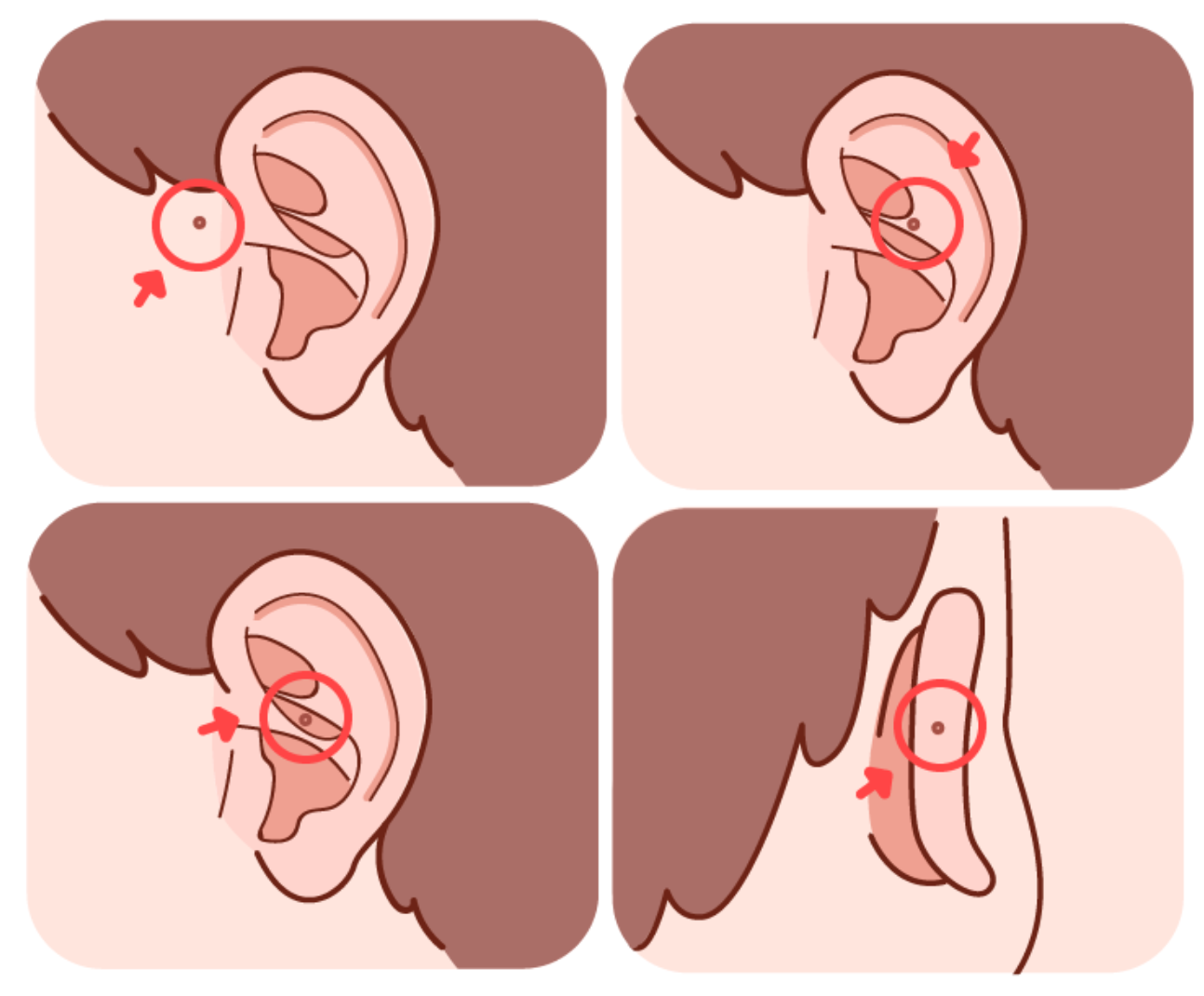
Image source: Dingxiang Mama
Is preauricular fistula common?
Yes, it is common. The prevalence of congenital preauricular fistula in China is 1.2%–2.5%, meaning that among every 1,000 people, 12–25 may be affected, with a higher incidence in females[1,4,5].
SYMPTOMS
What are the symptoms and manifestations of preauricular fistula?
Symptoms (patient's own sensations): Usually asymptomatic, but occasionally local itching or a small dimple on the skin near the ear may be noticed. If infection occurs, symptoms may include localized redness, swelling, pain, and pus discharge, often recurring and leading to scar formation[1,4].
Signs (observed by doctors during examination): Squeezing the small dimple may release a white, cheesy discharge with a slight odor. If infection is present, doctors may observe redness, swelling, warmth, and tenderness in the ear area, with a fluctuant sensation upon palpation.
Can preauricular fistula cause hearing impairment?
No[5].
This condition results from abnormal development of the auricle during the embryonic stage and does not affect the auditory organs, thus it does not cause hearing impairment.
CAUSES
Is preauricular sinus caused by negligence during pregnancy?
Preauricular sinus is not caused by a pregnant woman's negligence during pregnancy.
Preauricular sinus is an autosomal dominant genetic disorder resulting from abnormal development of the auricle during the embryonic stage.
Is preauricular sinus hereditary?
Yes, this condition is an autosomal dominant genetic disorder[1], meaning if either parent carries the dominant genetic gene for preauricular sinus, it may cause the fetus to develop this condition.
DIAGNOSIS
When should a preauricular fistula require medical attention?
Seek medical attention if the preauricular sinus shows signs of infection, such as localized skin redness, swelling, increased skin temperature, pain, or discharge.
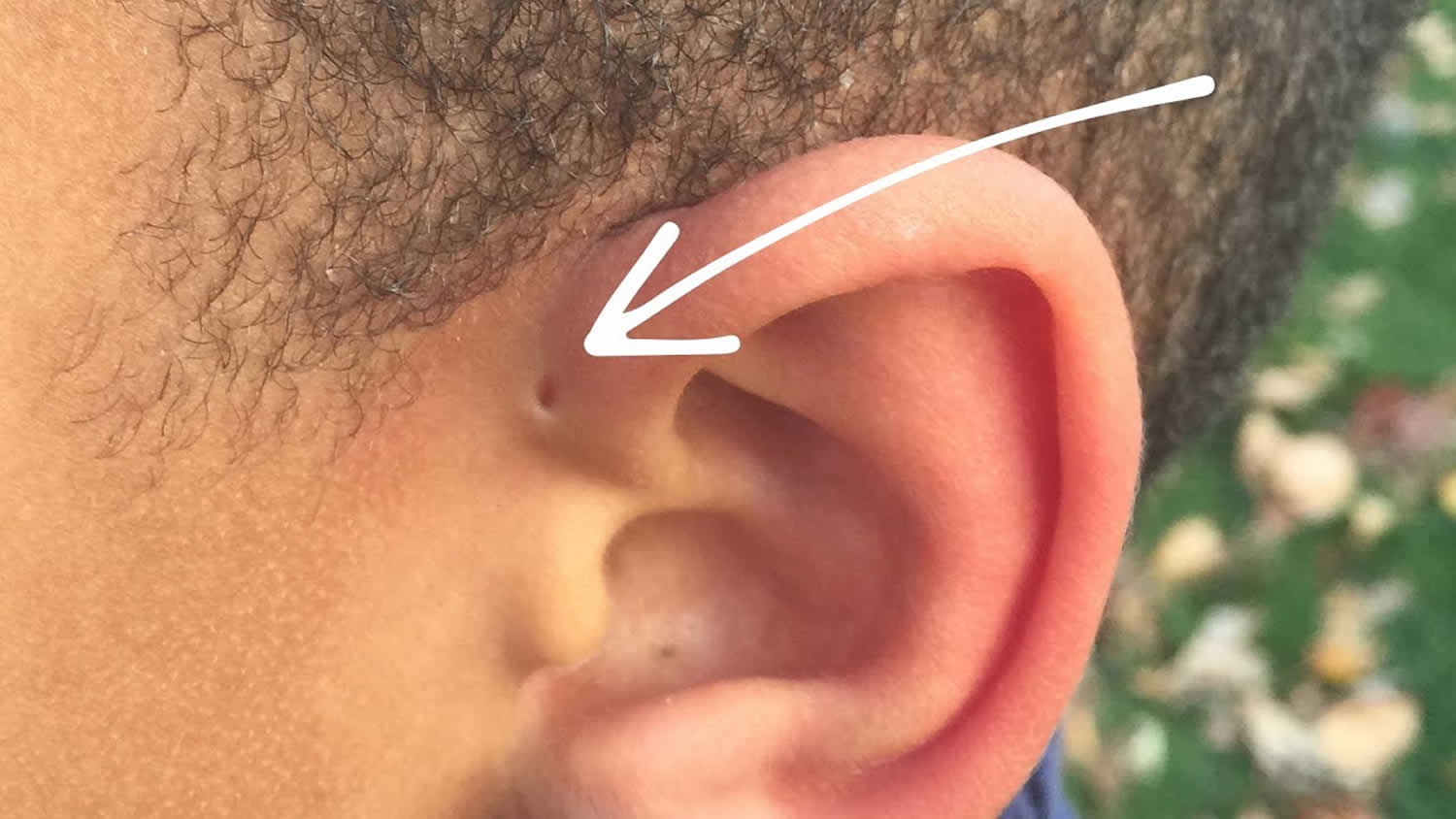
Small ear hole, image source: [4]
If the infection worsens, pus may form. As the abscess enlarges, it may rupture. Due to the potential depth of the fistula, self-treatment or puncturing is not recommended—prompt medical care is necessary.
Severe cases may require surgical intervention. Complete excision of the fistula is the only effective way to prevent recurrence.
What tests are needed if a preauricular fistula is suspected?
- Complete blood count (CBC): Recommended for patients with spreading infection, abscess formation, or fever to confirm infection. Elevated white blood cell counts indicate severe infection, warranting surgical consideration.
- MRI: Used for patients with abscesses to visualize the extent of infection (e.g., surrounding tissue involvement) and guide surgery.
- 3D ultrasound: Primarily employed to map the fistula’s internal spatial structure and its relationship with adjacent blood vessels[5].
TREATMENT
How to Treat Congenital Preauricular Fistula?
- Asymptomatic Cases Usually Require No Treatment
For babies with congenital preauricular fistula who show no symptoms or secondary infections, no special treatment is needed. Regular observation of symptoms is sufficient. Seek medical attention promptly if discomfort occurs [4].
- Medication
During acute infection of congenital preauricular fistula (with symptoms such as fever, swelling, pain, or pus discharge), antibiotics like cephalosporins (cefuroxime, ceftriaxone, etc.), penicillins (amoxicillin, ampicillin, etc.), or quinolones (levofloxacin, ciprofloxacin, etc.) may be prescribed under a doctor's guidance for anti-infection treatment.
However, the baby's age and individual condition must be evaluated before medication. A professional doctor should select the most appropriate drug, dosage, and administration method [4].
- Abscess Incision and Drainage
For babies with localized abscess formation, surgical incision and drainage can be performed at a hospital, followed by regular dressing changes under medical supervision until the infection is controlled and scar tissue forms [4].
- Surgical Treatment
For severe infections or cases with recurrent infections leading to scar tissue formation, doctors may recommend surgery. The main surgical methods for preauricular fistula removal include simple fistula excision and en bloc resection of preauricular tissue [5].
What to Do If a Preauricular Fistula Becomes Infected?
If a preauricular fistula becomes infected (with symptoms like redness, swelling, pain, or pus discharge), self-treatment is usually not feasible because antibiotics (prescription-only) or surgery are often required. Therefore, it is advisable to seek medical attention as soon as possible.
Patients in the acute infection phase need antibiotic treatment under medical supervision. For those with abscess formation, surgical incision and drainage should be performed at a hospital, followed by regular dressing changes until the infection is controlled and scar tissue forms [4,5].
- Simple Fistula Excision: The surgery takes 30–40 minutes, with sutures removed after 7–10 days. The wound is small, facilitating recovery. However, incomplete removal may lead to recurrence [4].
- En Bloc Resection of Preauricular Tissue: Suitable for patients with recurrent infections and scar tissue formation. The surgery duration varies, and suture removal depends on recovery progress (usually 7–10 days). Due to the larger wound, postoperative infection (e.g., fever) is possible.
Which Department Should Preauricular Fistula Patients Visit First?
Otolaryngology (ENT) or Head and Neck Surgery.
Does Preauricular Fistula Require Hospitalization?
Non-infected cases do not require hospitalization. Infected cases needing surgery require hospitalization.
What Is the Best Age for Preauricular Fistula Surgery?
The timing of surgery is not age-dependent but based on the patient's condition. Surgery is recommended for patients at risk of infection or those with controlled infections.
What Happens If Preauricular Fistula Is Left Untreated?
Untreated infected preauricular fistulas may lead to recurrent pus discharge, affecting daily life, or spread inflammation to surrounding tissues, causing infections in adjacent organs. Severe cases may be life-threatening.
Can Preauricular Fistula Be Cured?
Yes. With proper anti-infection treatment (1–2 weeks), infections can be fully controlled. Recurrent cases can be cured by complete fistula excision, with no impact on quality of life.
Can Preauricular Fistula Recur After Treatment?
After surgical removal, recurrence is unlikely. However, if surgery is not performed during infection or if excision is incomplete, temporary relief may occur, with a risk of recurrence.
DIET & LIFESTYLE
What should be paid attention to in daily care of preauricular fistula?
Daily care should focus on the following points:
-
Avoid squeezing and keep the area clean to prevent infection;
-
Do not poke it with foreign objects or sharp items;
-
When washing the face, clean the front and back of the ears with clean water;
-
After washing, gently wipe away surrounding moisture with a cotton swab, avoiding excessive force.
-
If the preauricular fistula has a secondary infection under treatment, a plastic protective cap can be worn during the baby's bath or hair wash to prevent wetting the wound dressing [6].
-
According to the authoritative medical database UpToDate, babies with preauricular fistulas should undergo regular hearing screenings, as these fistulas may be associated with certain abnormal syndromes.
-
Patients may experience social discomfort due to pus or foul-smelling discharge from the fistula. They should seek medical attention promptly to address the symptoms. Family and friends should also provide emotional support to help alleviate distress and maintain a healthy mental state, which aids in recovery.
PREVENTION
Can preauricular fistula be prevented?
Preauricular fistula is a congenital condition, and there are currently no effective preventive measures during pregnancy. However, after the child is born, it is important to maintain cleanliness and hygiene in the fistula area to avoid infection.
Expectant mothers should follow medical advice and undergo regular prenatal check-ups to monitor the development and health of the fetus, ensuring healthy growth. If any abnormalities are detected, they should be promptly and properly addressed.
